Reports of the decline of human interaction in the contact center are premature. While it might be a noble goal to obsolete phone calls, email, chat, and text, the need for dialog is still strong. Sometimes self-service fails. Some customers dislike self-service. Some transaction s are not well-suited to self-service. Whatever the reason for wanting or needing assisted service, customers trying to reach a human being all have one thing in common: they want to resolve their issues with as little effort as possible. Technology, applied effectively, can ensure each stage of the interaction cycle meets expectations and adds value.
The following diagram defines key steps in an interaction and highlights important considerations for an optimized experience along the way.
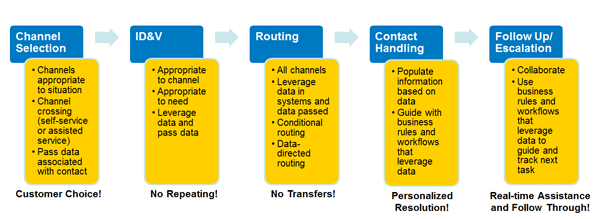
A wide variety of contact center tools come into play in making the best customer experiences happen. The following table maps the stages in the contact cycle to key technology enablers, and highlights some of these tools and how they apply.
|
Key Technology Enablers |
|||
| Stage in Contact Cycle | Leveraging Data | Business Rules/ Workflows | Channel Integration |
| Channel selection | Each channel offers ways to capture information actively (e.g., prompts) and/or passively (e.g., network information such as ANI and DNIS)
Data must move with the contact |
Business rules may “force” a channel change or exit from self-service, or define which channels are available for a particular situation | Customers start in their channel of choice – seeking direct assistance or first trying self-service (from which they may opt out or fail)
Must pass data so it’s available from channel to channel |
| Identification and Verification (ID&V) | Simplify ID&V by leveraging data
Pass data gathered and indication of successful verification |
Business rules can help define the level of ID&V needed for a given situation | Must pass data so it’s available from channel to channel |
| Routing/ Contact Delivery | Leverage basic data for conditionals and skills in ACD; use more advanced internal and external data for data directed routing in CTI | Every routing decision with a condition is a business rule, and business rules drive what to pop on arrival at the desktop | Multimedia routing engines apply to a variety of channels – voice, email, chat, text, social |
| Contact Handling | Data drives screen pops of customer information, knowledge presented, scripts, etc. | Business rules and workflows are leveraged significantly throughout contact handling – in CRM, scripting, KM, etc. | Contact handling should leverage what has already been done on other channels
Agents may shift a conversation from one channel to the next (e.g., chat becomes a call) |
| Follow Up and Escalation | Data can help define follow up or escalation needed (e.g., based on customer status) | Workflows in CRM or business process tools define downstream activities and accountability, or level of empowerment to complete an action | Agents may collaborate across channels during or after a contact through visibility to presence and use of IM, video, screen sharing |
These considerations and additional commentary can be reviewed by downloading the article, Assisted Service is Alive and Well.
